Azure Pricing Calculator
Overview of Azure Pricing Calculator:
- The Azure Pricing Calculator is a free tool by Microsoft that helps users to estimate the cost of using Azure cloud services based on their specific needs. It allows businesses and individuals to budget their cloud expenses efficiently.
Key Features & How It Works
1. Estimate Costs Easily:
- Helps you calculate the cost of various Azure services (e.g., virtual machines, databases, storage, networking).
2. Customizable Configurations:
- Adjust specifications like storage, computing power, and region to get a customized price estimation.
3. Compare Different Services:
- Allows side-by-side comparison of different Azure products to choose the most cost-effective solution.
4. Region-Based Pricing:
- Prices vary depending on the Azure data center region you select, helping you optimize for cost and performance.
5. Pay-As-You-Go or Reserved Pricing:
- Compare on-demand pricing vs. discounted reserved instances for long-term savings.
6. Export & Share Estimates:
- Download cost estimates as an Excel file to share with your team or clients for decision-making.
7.No Sign-Up Required:
- You can use the calculator for free without needing an Azure account.
Who Can Use It?
Developers planning cloud resources for their applications.
Businesses estimating operational costs before migration to Azure.
IT Teams comparing Azure pricing with AWS or Google Cloud.
How to use azure pricing calculator:
- If you are planning to move to the cloud with Microsoft Azure, one of the most important steps is accurately estimating your future cloud costs.
- Azure offers a powerful Pricing Calculator that helps you Calculate the costs of over 200 services, from virtual machines to databases, networking, and storage.
- However, beyond just adding products and checking basic cost estimates, there are advanced features and strategies you can use to get even more clear, realistic, and customized estimates.
- In this comprehensive guide, we’ll provide advanced tips, hidden features, and best practices for using the Azure Pricing Calculator.
Topics covered :
1. What is the Azure Pricing Calculator?
- An Azure Pricing Calculator is a free, web-based tool designed to provide detailed cost estimates for the services you plan to use on Microsoft Azure.
- Whether you’re creating a single virtual machine (VM) or an entire multi-region cloud infrastructure, the Pricing Calculator helps you make better-informed decisions by offering an upfront estimate of monthly costs.
2. Why to Use the Azure Pricing Calculator?
- Transparency: It allows you to get a clear understanding of costs associated with different services.
- Customization: You can estimate your specific needs, ensuring that the tool adapts to your actual cloud usage.
Predicting Costs: With Azure’s variable pricing models, this tool can help you avoid surprises on your cloud bill, especially when scaling or selecting different payment options.
3. How to Access and Set Up Your Azure Pricing Calculator:
- Step 1: Go to the Azure Pricing Calculator.
- Step 2: You do not need to log into an Azure account to use the calculator. You can start adding products directly.
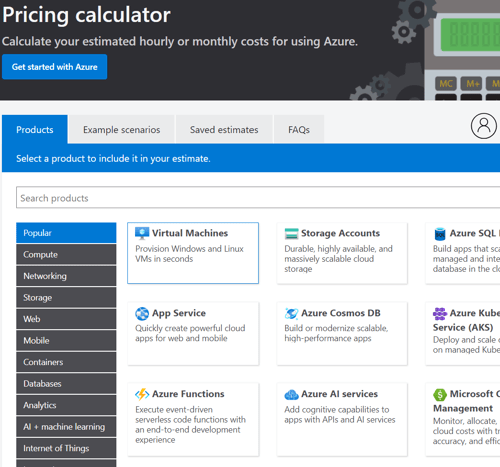
4. Step-by-Step Process for Using the Calculator:
Step 1: Choose the Right Products
Azure offers hundreds of different services. Choosing the right products involves:
- Categorization: Understand the different categories of services offered, such as:
- Compute (VMs, App Services, Functions)
- Storage (Blob Storage, Managed Disks, Backup)
- Databases (SQL, Cosmos DB, MySQL, PostgreSQL)
- Networking (Virtual Networks, Load Balancer, VPN Gateway)
- AI and Machine Learning
- Categorization: Understand the different categories of services offered, such as:
Step 2: Configure Your Products:
- Custom Configurations: After adding products, you can configure them by selecting the following:
- Instance Size: Choose the right VM size for your workload.
- Region: Azure pricing differs by region, so be sure to select the region where your services will be hosted. For example, VMs may cost more in a high-demand region like North Virginia than in a less populated region.
- Operating System: Azure VMs offer both Windows and Linux operating systems, which can impact costs, especially with licensing.
- Storage: Customize your storage choices. Depending on your workload, you may need SSDs (for high-performance applications) or HDDs (for cold storage).
- Scaling: Determine if you need autoscaling for your compute resources and configure scaling rules accordingly.
Step 3: Understanding the Different Pricing Models:
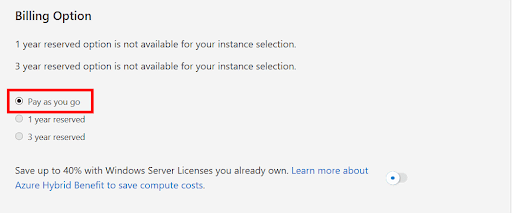
- Pay-As-You-Go: This is the most flexible pricing model, where you pay based on actual usage. However, it might be more expensive over time for predictable workloads.
- Reserved Instances: If you plan to use a service like a Virtual Machine for more than a year, consider Reserved Instances to save up to 72% compared to pay-as-you-go rates. You can select 1-year or 3-year terms.
- Example: A 3-year reserved instance could significantly lower costs, but you must commit upfront.
- Spot Pricing: Azure also provides Spot VMs for non-production workloads. These VMs offer steep discounts but can be interrupted at any time.
Pro Tip: Always check whether Reserved Instances will be more cost-effective for your long-term usage.
Step 4: Use Pricing Scenarios for Complex Estimates:
- Multiple Configurations: If you have more complex workloads, you can create multiple estimates for different configurations to compare costs.
- Scaling Scenarios: If you anticipate growing your infrastructure over time, use the scalability options to forecast the cost increase when you add more resources. This is especially helpful for estimating costs in high-traffic applications or seasonal workloads.
Example: You might start with 2 VMs but need to scale to 50 VMs in a year. Use the calculator to model this growth.
Step 5: Factor in Hidden Costs: Networking, Storage, and Backup:
- Networking Costs: Don’t forget that networking, especially data transfer between regions or between your on-premises infrastructure and Azure, can add up. Estimate costs for VPNs, load balancing, and data egress.
Backup and Disaster Recovery: Consider adding Azure’s Backup or Site Recovery services to your estimate, especially for critical workloads.
Step 6: Use Additional Tools to Refine Your Estimate:
- Azure Cost Management + Billing: Use this tool alongside the Pricing Calculator to monitor and optimize your Azure spending. Cost Management provides insights into your usage and can track your estimate against actual spend.
Azure TCO Calculator: For organizations migrating from on-premise infrastructure to Azure, use the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Calculator. It compares your existing infrastructure costs to the estimated costs on Azure.
5. Advanced Tips and Strategies for Accurate Cost Estimation:
- Estimate Data Storage Growth: For storage-intensive applications, factor in data growth over time. Azure provides options to estimate incremental increases in storage capacity, such as in database solutions like Azure SQL Database.
- Consider License Mobility: If you have existing Microsoft licenses (for Windows Server, SQL Server, etc.), you may be eligible for Azure Hybrid Benefit, which reduces your overall cost.
- Monitor Billing Alerts: After configuring your estimate, set up cost alerts within Azure’s Cost Management to receive notifications when you approach budget thresholds.
6. How to Export, Save, and Share Your Estimates:
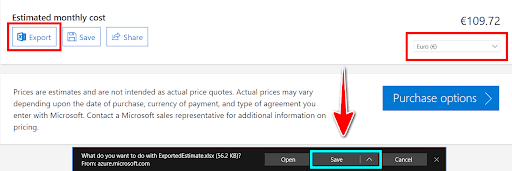
- Save Estimates for Future Use: You can save estimates in your Azure Portal for future reference or for cost tracking across multiple projects.
Export to Excel: The Azure Pricing Calculator allows you to export estimates to Excel for detailed analysis, making it easier to share with teams or management.
7.Why Choose Azure Pricing Over AWS and GCP?
- When it comes to selecting a cloud provider, businesses often debate between the big three: Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Each has its strengths, but Azure’s unique pricing model and benefits make it a particularly compelling choice for many users.
- Let’s see why Azure might be the right fit for you especially in terms of pricing.
1. Integration with Microsoft Products:
If your organization already uses Microsoft products (Windows Server, SQL Server, Active Directory, Office 365, etc.), Azure provides seamless integration.
- Azure Hybrid Benefit: One of the biggest advantages for organizations already invested in Microsoft products is Azure Hybrid Benefit. This program allows you to use your on-premises Windows Server and SQL Server licenses in Azure, often saving up to 40-50% on virtual machine costs.
- Familiarity: For teams already familiar with Microsoft tools and interfaces, Azure’s interface and services are easier to integrate, manage, and maintain, which can ultimately reduce training costs and speed up implementation.
How this affects pricing: You won’t have to pay full price for Microsoft software in the cloud, and you’ll be able to leverage existing investments in Microsoft technology.
2. Competitive Pricing with Reserved Instances:
While all cloud providers offer some form of reserved instances, Azure stands out with its pricing flexibility and discounts.
- Azure Reserved Instances (RIs): Azure offers up to 72% savings on virtual machines (VMs) if you commit to a one- or three-year term. This is similar to AWS, but Azure’s pricing for RIs is often considered more competitive when it comes to Windows Server-based workloads, especially when combined with Azure Hybrid Benefit.
- Pay-as-You-Go: For users who need flexibility, Azure’s pay-as-you-go pricing model allows businesses to scale their services up or down easily without any long-term commitment.
How this affects pricing: If your organization has predictable workloads, opting for Azure Reserved Instances can result in significant savings compared to other cloud providers.
3. Focus on Enterprise and Hybrid Cloud Solutions:
Azure is often the preferred choice for large enterprises and businesses looking for hybrid cloud solutions. This is due to Azure’s extensive hybrid cloud capabilities and focus on enterprise-grade services.
- Hybrid Cloud: Azure’s Azure Arc and Azure Stack services allow businesses to run and manage hybrid cloud environments—meaning you can extend your on-premises systems to the cloud while still managing everything in one unified platform.
- Compliance and Security: Azure is known for its strong security measures and compliance with industry standards, which is important for industries like finance, healthcare, and government. Its pricing reflects the enterprise-grade security and compliance tools it provides.
How this affects pricing: While hybrid solutions might collect additional costs, they provide value by allowing businesses to run their workloads in the best environment, whether on-premises or in the cloud, which could lead to cost savings in the long term by optimizing resource usage.
4. Global Reach and Data Center Options:
Azure has a massive global presence with over 60 data centers worldwide, which is more than AWS and GCP. This vast network allows businesses to choose where their data is hosted and ensure low latency for global users.
- Regional Pricing Variability: Like AWS and GCP, Azure’s pricing varies by region, but Azure allows you to choose a region with lower costs for the same service, providing an opportunity to save money.
- Data Sovereignty: If your business requires data to remain in specific countries or regions due to legal or regulatory requirements, Azure’s extensive global network can help minimize data transfer and compliance risks.
How this affects pricing: Azure’s broad regional coverage allows businesses to strategically choose regions that not only meet their legal requirements but also offer lower operating costs, optimizing pricing in the process.
5. Strong Support for Open-Source and Multi-Platform Environments:
While AWS and GCP are known for being developer friendly and open source ready, Azure has also made significant strides in supporting open-source technologies.
- Cross-Platform Flexibility: Azure supports multiple operating systems, including Linux and Windows, and is optimized for multi-cloud environments. So, if your infrastructure spans multiple platforms or you want to use a combination of AWS, GCP, and Azure, Azure provides tools that work across all of them (such as Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)).
- Developer Tools: Azure also offers extensive developer tools, like Visual Studio, GitHub, and Azure DevOps, making it easier for teams to build and deploy applications.
How this affects pricing: Azure’s ability to work with open-source technologies and across platforms provides flexibility without forcing businesses into a specific tech stack, allowing them to optimize costs based on their existing infrastructure.
6. Transparent and Predictable Cost Management:
Azure’s Cost Management + Billing tool is very powerful and offers detailed insights into how resources are consumed and how costs are gathered across services. Azure allows you to:
- Set Budgets and Alerts: You can set custom budgets and receive notifications if you approach your spending threshold. This proactive approach helps ensure that you don’t experience unexpected cost spikes.
- Cost Analysis Tools: The Cost Management tool provides a breakdown of your usage patterns, so you can better understand where you’re spending money and optimize usage accordingly.
How this affects pricing: Azure’s ability to track, forecast, and control costs provides greater visibility and more control over cloud spending, which helps businesses avoid surprises and stay on budget.
7. Azure’s Strong AI, Machine Learning, and Data Analytics Services:
Azure has some of the best pricing models for AI and machine learning workloads, which are becoming increasingly important for modern businesses.
- Azure AI and ML: With offerings like Azure Machine Learning, Cognitive Services, and Azure Databricks, businesses can access powerful AI tools at competitive rates. Azure’s AI pricing is often considered more cost-effective for startups and small-to-medium businesses when compared to AWS’s offerings.
- Data and Analytics: Azure’s data services, like Azure Synapse Analytics and Azure Data Lake, offer comprehensive analytics tools at a reasonable cost, especially for large datasets. Azure also has strong integration with Power BI, making it an attractive option for businesses focused on business intelligence.
How this affects pricing: Azure’s pricing models for AI and data analytics allow businesses to scale up as needed without having to pay premium prices, making it an affordable choice for businesses looking to leverage these emerging technologies.
Conclusion
- Cost-Effectiveness: For businesses already using Microsoft products, Azure offers a unique pricing advantage with its Hybrid Benefit program and more competitive Reserved Instance pricing.
- Hybrid and Enterprise Support: Azure excels in offering hybrid cloud solutions that are tailored to large enterprises with complex needs.
- Global Reach and Flexibility: Azure’s vast network of global data centers allows you to select cost-effective regions and ensure low-latency performance.
- Predictable Costs: With Azure’s advanced cost management tools, you can keep your cloud expenses predictable and under control, avoiding unexpected charges.
- Developer and Open-Source Flexibility: Azure offers a flexible environment for developers with multi-platform support, cost-effective AI solutions, and integration with tools like GitHub and Visual Studio.
Additional Resources:
FAQ's About AzurePricing Calculator
Here’s how it works: Product Configuration – The calculator pulls the per-unit pricing for each product from the Azure Retail Pricing API based on the different product parameters selected by the user such as: region, size, operating system, tier, and other specific features.
Select Cost Management and then Cost analysis. Select your subscription or another scope. Next, create a Daily Costs view, and change the Group by to show costs by Meter so that you can see each the costs from each feature. The meter names for each Azure Monitor feature are listed here.
The TCO Calculator only considers direct costs, while the Pricing Calculator includes indirect costs like maintenance or operating costs. The Pricing Calculator estimates the costs of a specific Azure configuration, while the TCO Calculator is used for comparison with an on-prem configuration.
anyone can use the TCO. Using TCO don’t need any subscription.
- Running Windows instances on AWS can be up to 5X more expensive than using your existing Windows SQL Server and SQL licenses with Azure.
- Azure Cost Analysis is a feature provided by Microsoft Azure, one of the world’s leading cloud service providers, as part of the Azure Cost Management tool. Azure Cost Analysis allows you to monitor, allocate, and optimize the cost of Azure resources.
- Microsoft offers three main ways to pay for Azure VMs and other cloud resources: pay as you go, reserved instances, and spot instances.
While CapEx involves upfront investments in physical infrastructure and has long-term implications, OpEx offers flexibility, scalability, and cost control through pay-as-you-go pricing.
TCO is a calculation performed to estimate the total expenses associated with a particular asset. It measures all money spent on acquisition, implementation, use, and disposal or discontinuation of a product or equipment.

